Pipe
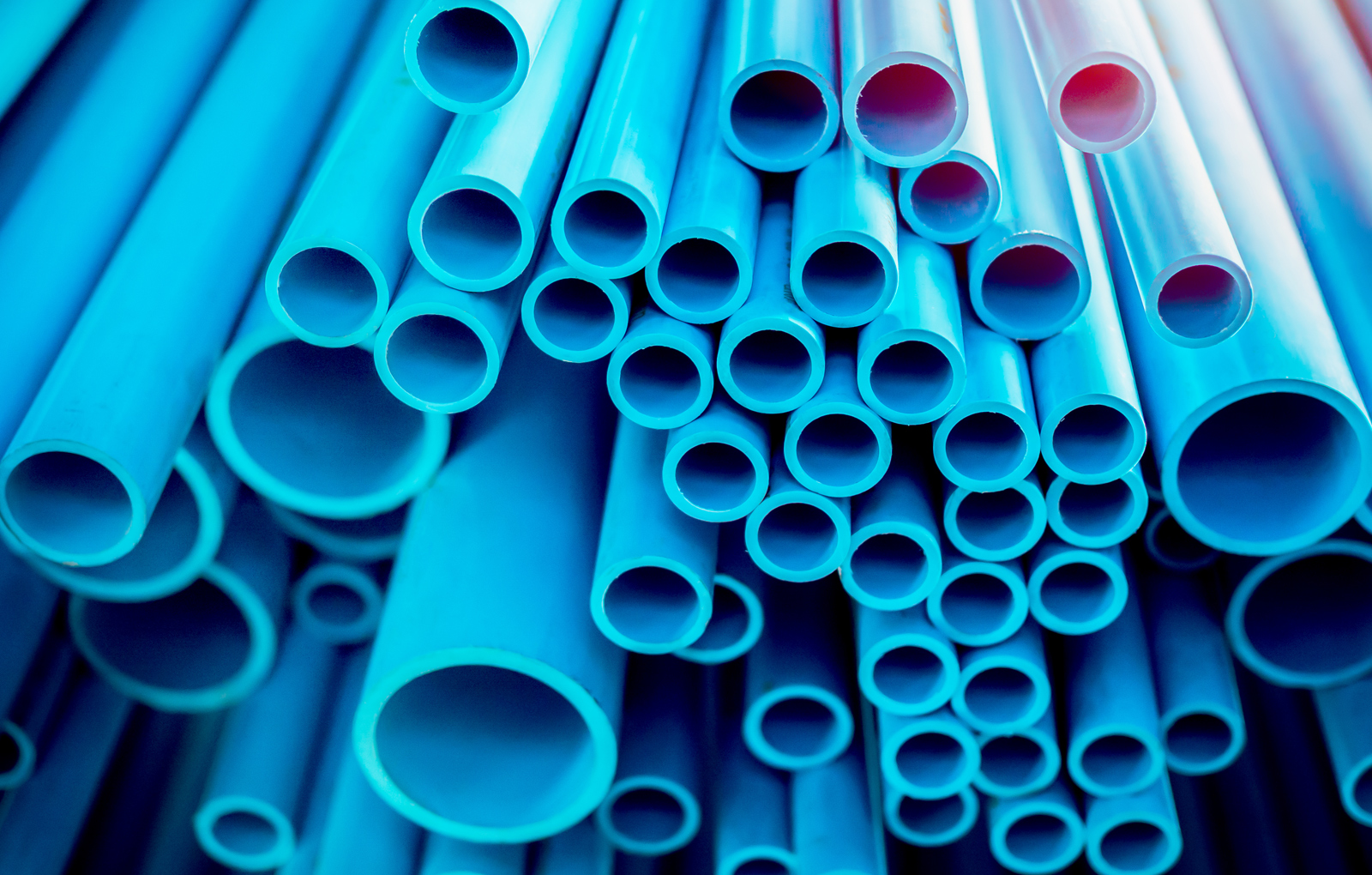
At Euroviti, we have a dual range for the production of pipes: the twin-screw, used for processing RIGID PVC, ideal for the production of tubes mainly intended for drainage and water supply, and drainage. The single-screw, on the other hand, is suitable for all other materials such as PLASTIFIED PVC, PE, PP, HDPE, EVA, ABS, PEXL, used to obtain various types of pipes for different uses, such as heating systems, hydraulic systems, air conditioners, and other fields of application.
Profile
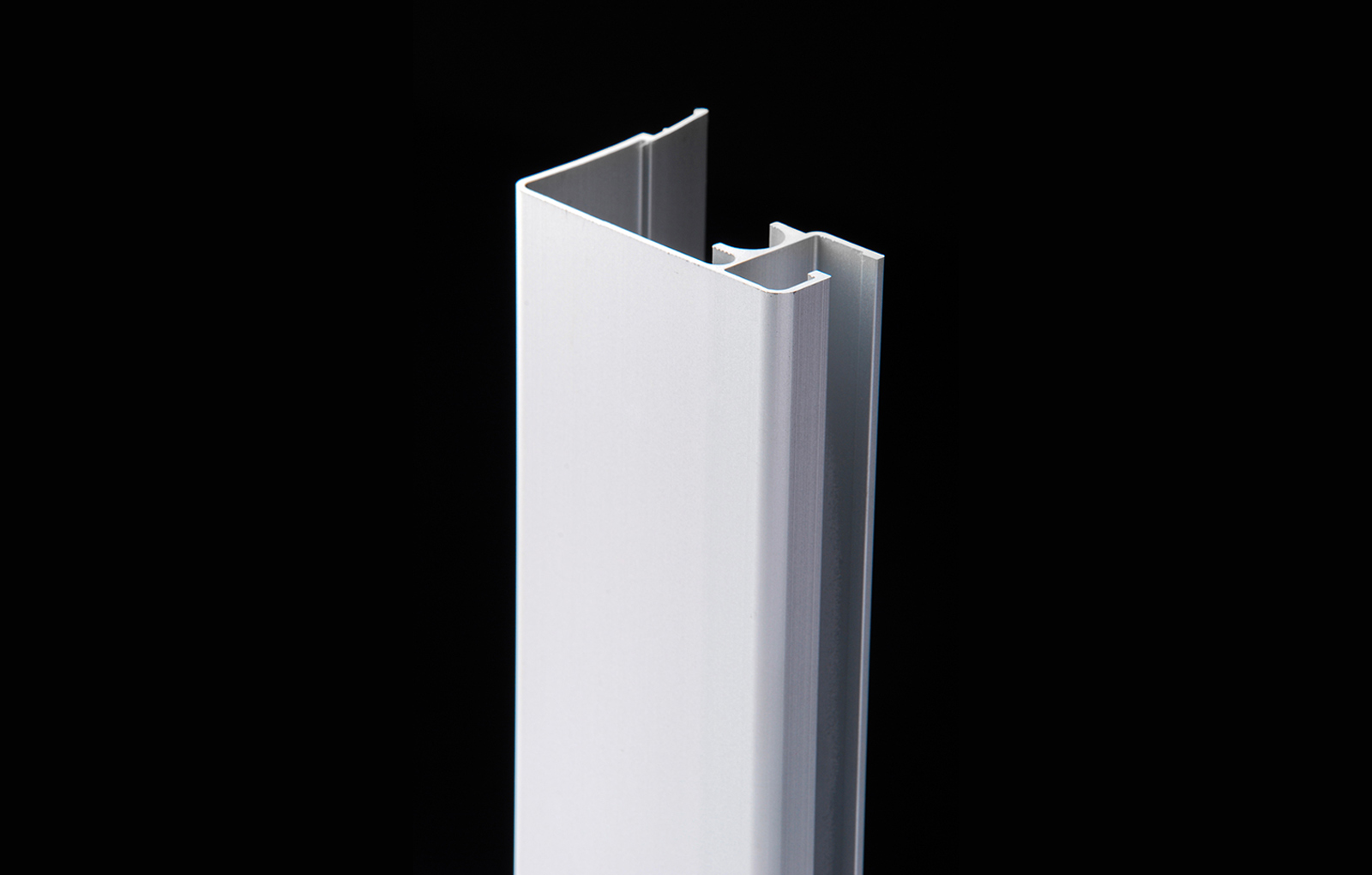

Euroviti’s mission is to provide our customers with high-performing screw profiles, specifically adapted to work with every type of material, in order to enhance their qualitative characteristics. We offer two versions of screw profiles, one for the conical twin-screw and the other for the single-screw.
Film


Film can be distinguished into Blow film or Cast film, and the commonly processed materials are PE, PP, PVC. The materials commonly processed in these areas include PE, PP, PVC, PA, PLA, Materbi, HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, and MDPE. These are often combined with percentages of regrind material, master batch, and numerous other additives.
The screws used in this sector vary from 28 to 35 L/D. The choice of the adopted profile depends on the available length expressed in L/D and typically involves a complex profile with various specificities.
In the two macro-categories, Blow film and Cast Film, single-screw extruders are used, consisting of a barrel, a feed block with an internally grooved sleeve, and a screw.
Furthermore, there are applications, albeit in limited numbers, for the production of blow film in Rigid PVC. These are processed with twin barrels and counter-rotating parallel twin screws, generally offered in nitrided steels or bimetallic alloys.
Compound

In the production of compounds, twin-screw extruders are predominantly used. These include both parallel counter-rotating and co-rotating models, with the latter capable of reaching lengths beyond 50 L/D.

Recycling
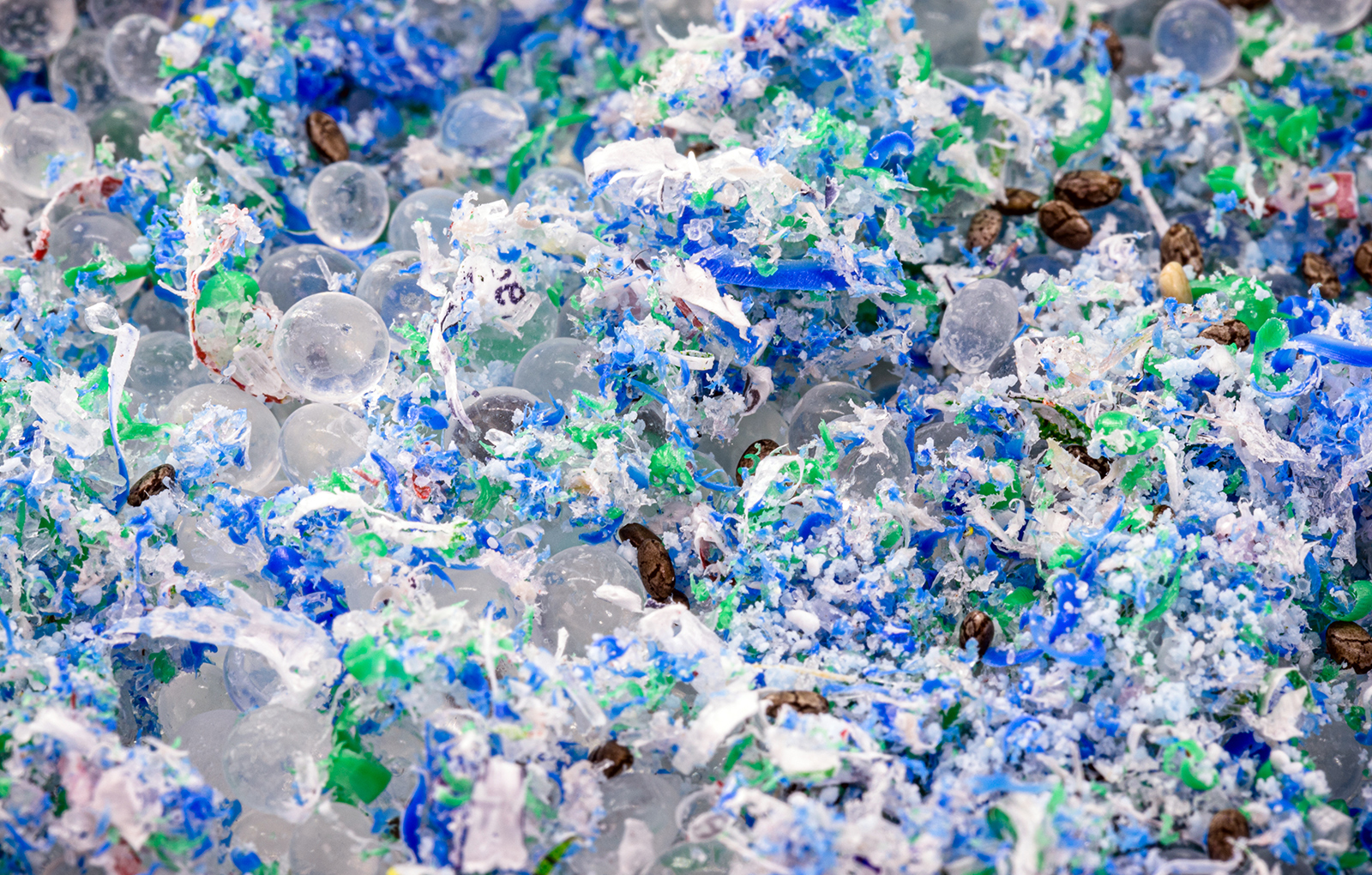


In the recycling sector, Euroviti works with common materials such as PE, PP, PS, PMMA, ABS, PC, PLA, PVC, XPS, PET, and ABS. These materials come from both post-industrial and post-consumer processes.
To be recycled or regenerated, the waste materials are first regrind, washed, cleaned, and dried, and then introduced into the hopper, either in their original form or densified. Depending on specific needs, the screw used can have a simple profile, be equipped with one or more mixers, and have a barrier profile. The lengths vary between 37 and 54 L/D, depending on the type of regrind material being processed. In versions with higher L/D, it is essential to equip the screw and the barrel with a dual degassing system to completely eliminate residual moisture.
Given the heterogeneous nature of the regrind material, the set of equipment we recommend is highly resistant. The barrel in EUV400, a bimetallic alloy, and the screw in EUV60, with a Nickel-based alloy coating, ensure the long-lasting efficiency of the plant. In cases of more severe wear, we suggest the extrusion set with barrel and screw in Tungsten Carbide-based alloys, respectively EUV1000W and EUV83.
Blow Molding

Blow molding is a technology used for the production of hollow items such as bottles, containers for oils, cosmetic products, and automotive articles. This technique employs various materials in the form of granules, powder, additives, and regrind materials.
The screws used in this sector have an average length of 24 LD. They can have standard profiles, with mixers, maddocks, or barrier, depending on the type of plastic material, the percentage of regrind material, and masterbatch being used. To meet the demands for process maximization, we offer exceptionally high-performing extrusion sets with L/Ds longer than the average. These sets are equipped with special screws, like the HPE, and matched with barrels featuring cooling and helical grooves in the feeding area.
We have introduced a new technology that allows for the implementation of spiral grooves inside the barrels for 20 L/D. This innovation significantly reduces the overall dimensions and size of the line, promoting considerable energy savings and thus reducing production costs.

Cable
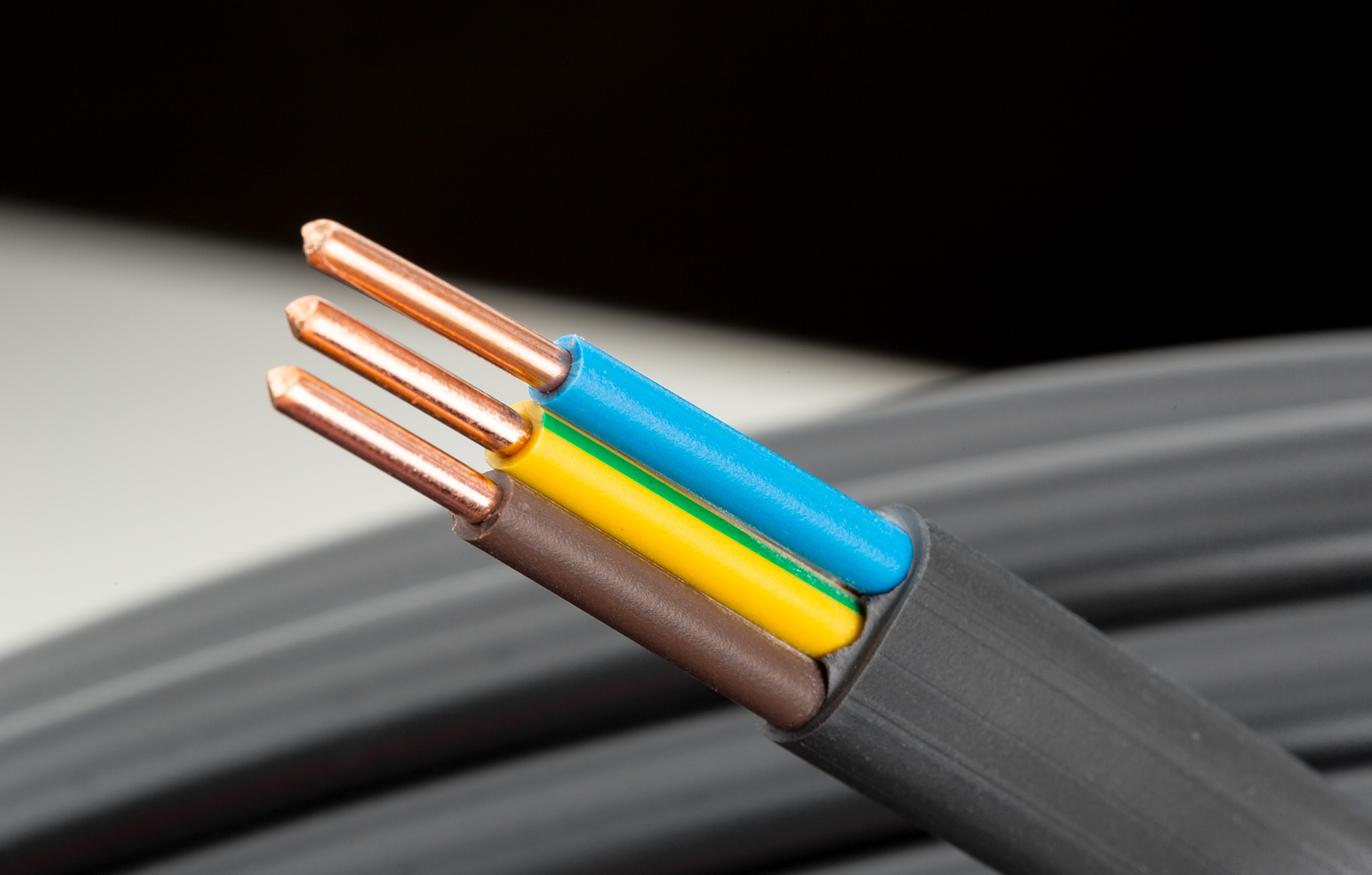
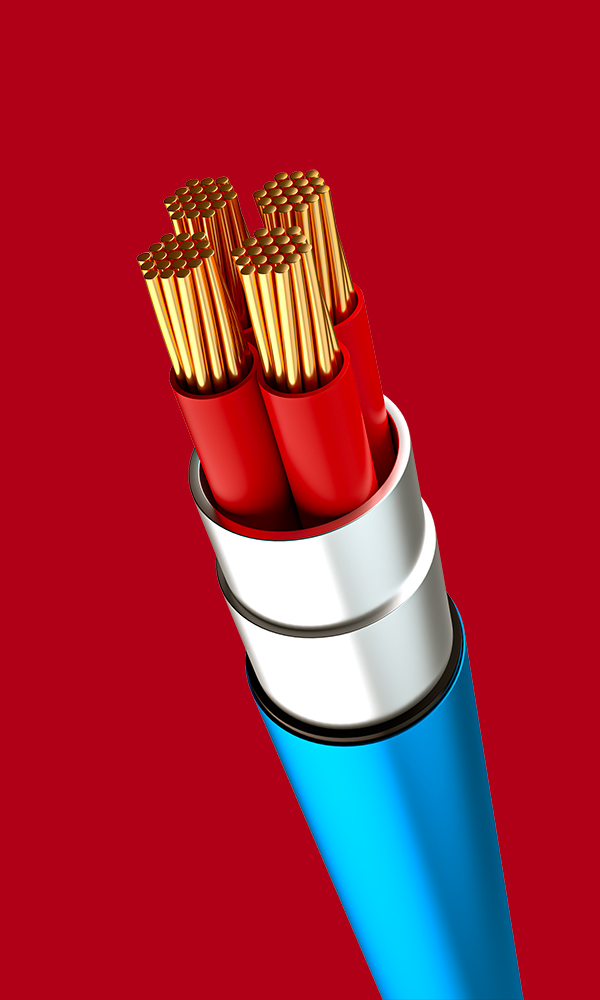
In cables’ production, it is common to use a variety of materials such as PE, PP, PVC, PU, EPDM, etc. The screws used in these processes typically have an L/D ratio ranging from 25 to 30.
The choice of screw design is crucial for the efficiency of the extrusion process. These designs range from standard profiles to those with mixers, up to barrier profiles, like the HPE, designed to improve plasticization and the homogeneity of the material. When it comes to working with more specific and particular materials, like HFFR or EPDM, it is essential to select the appropriate screw profiles. In these cases, we propose less complex screw profiles, which have proven to be key to success. These screws are particularly effective in handling the peculiarities of these materials, ensuring an efficient production process and superior quality products.
For cable production as well, the barrel can be monolithic or with a separate feed block and an internally grooved sleeve. We offer these configurations in both nitrided and bimetallic versions.
Tire

Tire production occurs through an extrusion process that uses a single-screw. The starting material normally consists of “rubber strips,” a blend of over 10 different rubber compounds, both natural and synthetic, enriched with fillers such as silicon, carbon, gypsum, etc. After extruding and covering the tire structure, the product goes through a vulcanization phase in specific molds. This process gives the tire its distinctive and particular geometric shape.
Tires are generally processed with medium and large size barrels and single-screws, with a relatively short L/D ratio to preserve the final quality of the extruded product. A distinctive feature of the screw design used is the profile with two interrupted principles, which allows the attachment of mixing pins directly onto the barrel. These screws have a design with a particular volume and a low or non-existent compression ratio (RC), chosen to ensure a high production capacity (kg/h). This optimized configuration ensures the efficiency of the production process and the quality of the finished product.
The barrel is generally composed of 4 parts: the feed block and sleeve, the outer body of the barrel which acts as a cooling circuit, plus an incorporated sleeve. The proposed versions include both nitrided and bimetallic. For the screws, in addition to the nitrided version, we also offer models with wear-resistant coatings, such as EUV56/EUV60/EUV83.

Sheet


Extrusion of sheet requires thicknesses varying from tenths of a millimeter to millimeters. To ensure that the plates are free from shades and bubbles, we recommend the use of a degassing screw profile, ideal for eliminating any form of moisture and residual gases.
To improve the quality of the melt in this area, we propose a screw profile with an incorporated mixer. In some specific cases, we suggest the insertion of a barrier profile, such as the HPE. The barrel is generally equipped with a feed block with a grooved sleeve in the feeding zone. The versions of barrels we offer are the classic nitrided steel or bimetallic alloys.
Rubber

Among the silicone rubbers commonly used in the industry, EPDM, EPR, NBR, and SBR are the most widespread. These rubbers, both synthetic and natural, can be fed in two main formats: as “strip/ribbon” or in granule form. The choice of format depends on the type of process used.
The processing of these rubbers can occur through extrusion or injection, using specific screws for each method. The available screws, including the standard profile, fall into the macro families HPS-HPB-HPE, depending on whether it is molding or extrusion. These are characterized by a low compression ratio and short L/D. In the extrusion section, the sets are generally composed of a barrel divided into four parts: feed block and sleeve, the outer body of the barrel which acts as a cooling circuit, plus an incorporated sleeve, available in both nitrided and bimetallic versions. For the screws, in addition to the nitrided version, we also offer models with wear-resistant coatings, such as EUV56/EUV60/EUV83. In the injection section, the sets are generally composed of barrel and screw, offered in both nitriding steels and the bimetallic version.

Expanded Foam


In the production of expanded materials, such as foam, the extrusion of polymers like Polyethylene and Polystyrene (XP) can be carried out in two ways: by using a chemical blowing agent included in the granule or through the injection of gas. The goal of this process is to develop a spongy material, used for its thermal and acoustic insulation properties or as a filler material, depending on specific needs. Tandem systems are generally configured as two-stage plants. The first stage, primary, manages the process of plasticization, mixing, and the insertion of the blowing agent. This can be achieved with self-cleaning single-screw or co-rotating twin-screw extruders. The second stage is connected via a manifold and deals with the cooling of the material.
Depending on the type of extruder used, whether twin-screw or single-screw, we are able to provide high-tech replacement components, suitable for any type of blowing agent used.
Injection Molding
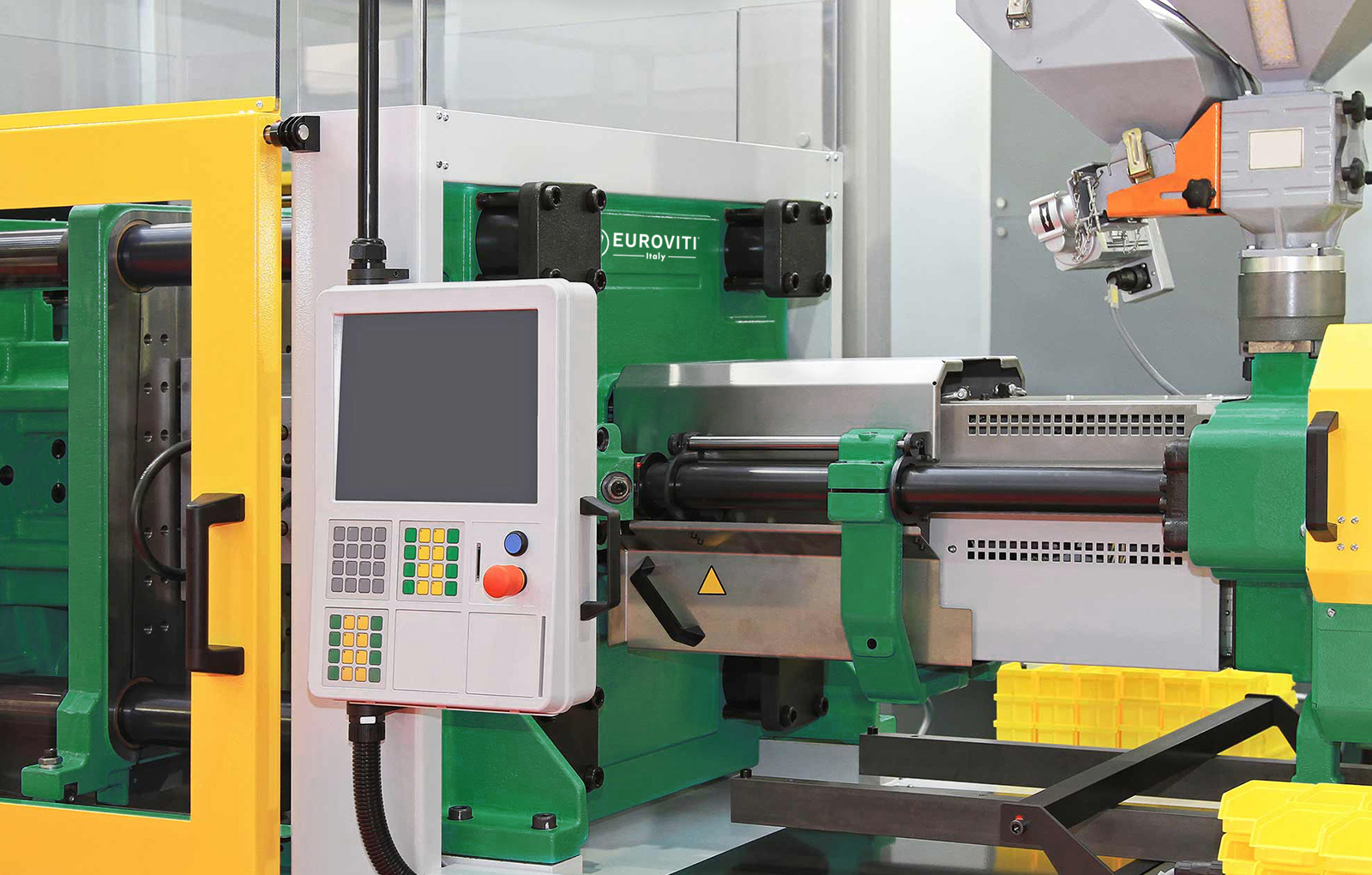

In the field of injection molding, Euroviti’s screws have a length ranging from 18 to 28 LD and are generally equipped with standard profiles. Our recent studies have led to the development of new high-performance profiles, such as HPS and HPB, which allow the use and processing of regrind materials up to 100%. These are particularly suitable for the production of fruit and vegetable crates and common-use containers.
Screws with a high L/D and equipped with the HPB profile allow high speed with significantly reduced cycles. For the most requested special applications, we offer some innovative solutions: the “degassing” profile, necessary to remove the moisture present in the granule/regrind material, and gas introduction systems for the molding of expanded components.
Anti-corrosive and wear-resistant solutions are among the most requested in this sector. About 90% of our production is based on bimetallic sets.

Food Industry
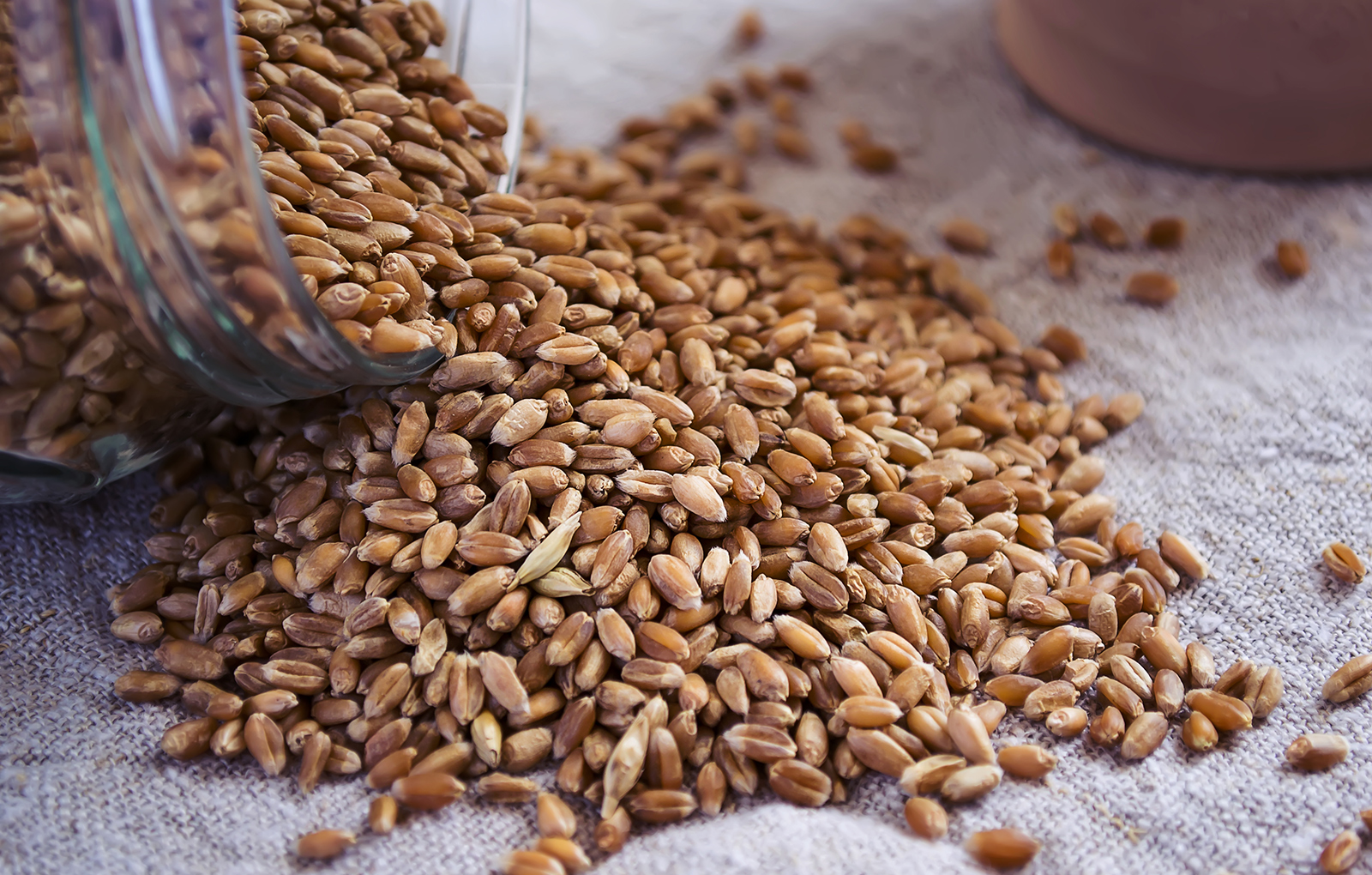


The cereal processing process involves the use of temperatures ranging from 30°C to 120°C. During this process, the cereals are extruded, compacted, and drawn to produce bars, snacks, and pasta.
CONTACT US
Tell us what you need
Follow us












